CSpeak - The Commands Editor
Commands
Hierarchy
In CSpeak v6 and earlier the list of instructions used by a command was contained in a linear list that was enumerated each time the command was run or opened. This provided a very simple way for users to create commands that were easy to understand, however in this simplicity we lost the ability to create more interesting commands. Items like error checking and conditional branching were removed because those concepts were generally too complex for the average provider to understand.
What we found in CSpeak v6 was that most sites do not create commands on their own anymore. The strong majority of users use commands created for them and in most cases those commands are pretty simple (e.g. type a quick text). Since most users are not building commands and the handful that are, tend to be more advanced users looking to build more advanced functions we are reevaluating our position on commands.
With CSpeak v7 we are moving away from a linear list and moving to what is now as a tree structure. A tree is a collection of nodes that point to nodes under it. This allows for the traditional linear style of command, but also allows for users to build branching commands that can run specific functionality for specific conditions. A simple example of this is conditions based on text control.
For example, consider a command that inserts text into a field. A user may want to insert text one way if FTC is available or use something generic like the clipboard if BTC is available.
Properties
Name | Type | Description |
ID | Int | The numeric ID that identifies this object in AppLink. |
Name | String | The name of this command. [Required] |
Spoken Forms (CSV) | String | The collection of spoken forms separated by a comma. If no spoken forms are provided this command can only be invoked hotkey or microphone button press. |
Instructions | Object | The starting node of the instruction tree. This is stored as a string in the database and not as individual records. This is done to help with lookup speed. |
Registers
Registers are positions in memory that allow the user to store values of specific types. The registers are not directly accessible by the user. The user can only access registers by calling a relevant instruction. This is a new concept for the generation 7 ecosystem to help expand the available functionality and usability of commands.
Type | Description |
Automation Element | This register holds the last accessed automation element |
Text Control | This register holds a mapped text control that is converted from the automation element register. |
String | This register holds a single .NET string value. |
Selection | This register holds a selection object. |
Enumerations
EDictationBoxMode
Name | Value |
Undefined | -1 |
Normal | 0 |
Express | 1 |
EDictationMode
Name | Value |
Undefined | -1 |
Auto | 0 |
Dictation Box | 1 |
Basic | 2 |
EMouseButtons
Name | Value |
Undefined | -1 |
Left | 0 |
Right | 1 |
ERecordingMode
Name | Value |
Off | 0 |
On | 1 |
Application Namespace
Exit
Description: This instruction type will immediately stop recording and close CSpeak.
Log
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction type will add a message to log.
Open Settings
Description: This instruction type will open the main window.
Run
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction type will attempt to start a process by name. It is usually best to test this functionality with the Run utility found in Windows.
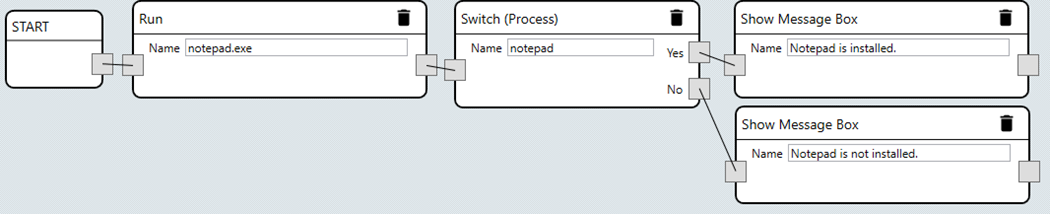
Show Message Box
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction type will show a message box with the provided message.
Wait
Arguments: Int
Description: This instruction type will halt processing on the main thread for the provided number of milliseconds.
DAX Copilot Namespace
Copy Section
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction will copy the section (by name) into the clipboard.
Insert Section
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction will insert the section (by name) into the active edit control.
Open AutoPilot
Description: This instruction will open the DAX Copilot dialog.
Control Structures Namespace
Loop
Arguments: Int
Description: This instruction type will allow you to run a branch of instructions for a specified number of loops.
Switch By Dictation Mode
Description: This instruction type will allow you to branch the instruction flow based on what dictation mode the client is currently in. Basic mode is not currently supported with this instruction.
Switch By Pattern
Arguments: Int
Description: This instruction type will allow you to branch the instruction flow if you the automation element in the automation element register has a certain pattern. The argument provided is the programmatic ID of the automation pattern.
Name | ID |
Invoke | 10000 |
Selection | 10001 |
Selection Item | 10010 |
Text | 10014 |
Toggle | 10015 |
Value | 10002 |
Switch By Process Name
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction type will allow you to branch the instruction flow if you are in a specific process.
Switch By Text Control
Description: This instruction type will allow you to branch the instruction flow based on the text control available to the text control in the text control register.
Speech Kit Namespace
Set Dictation Box Mode
Arguments: Int
Description: This instruction type will allow you to set the mode of the dictation box. The argument should be the integer value of the dictation box mode.
Set Dictation Mode
Arguments: Int
Description: This instruction type will allow you to set the mode of the client. The argument should be the integer value of the dictation mode.
Set Recording Mode
Arguments: Int
Description: This instruction type will allow you to set the recording mode. The argument should be the integer representation of the Boolean value.
Show Dictation Box
Description: This instruction type will show the dictation box if the client is currently in the dictation box dictation mode.
Toggle Dictation Mode
Description: This instruction type will toggle the client between the auto and dictation box dictation modes.
Toggle Recording Mode
Description: This instruction type will toggle the client between recording modes.
Transfer Text
Description: This instruction type will invoke the transfer text command used by the dictation box if the client is in the dictation box dictation mode.
Use Command
Arguments: Int
Description: This instruction type will allow you to invoke a separate command.
Text Control Namespace
Accept Defaults
Description: This instruction type will invoke the accept defaults command on the text control in the text control register.
Bring to Front
Description: This instruction type will attempt to bring the text control in the text control register to the foreground and give it keyboard focus.
Field Complete
Description: This instruction type will invoke the field complete command on the text control in the text control register.
Get Text
Description: This instruction type will invoke the get text command on the text control in the text control register. The result will be placed in the string register.
Get Text Control
Description: In auto mode, this instruction type will attempt to map the automation element in the automation element register. The result will be placed in the text control register. In the dictation box mode, this instruction type will place the dictation box in the text control register.
Get Locked Text Control
Description: In auto mode, this instruction type will set the text control register to the text control that has been focus locked. The result will be placed in the text control register. In the dictation box mode, this instruction type will place the dictation box in the text control register.
Insert Text
Arguments: String
Description: In auto, this instruction type will invoke the insert text command on the text control in the text control register. The string argument can use the following placeholders.
Name | Description |
{d} | The date component of the DateTime.Now object. |
{t} | The time component of the DateTime.Now object. |
{dt} | The date and time components of the DateTime.Now object. |
{cb} | The contents of the clipboard. |
{ldr} | The last dictation result. In manual mode this will recover the full last transfer. |
Lock Focus
Description: This instruction type will tell the Virtual UI to lock focus on the currently focused text control. This will not be released until recording stops or the unlock focus instruction is invoked.
Next Field
Description: This instruction type will invoke the next field command on the text control in the text control register.
Previous Field
Description: This instruction type will invoke the previous field command on the text control in the text control register.
Set Selection
Arguments: Int, Int
Description: This instruction type will invoke the set selection command on the text control in the text control register. The first argument is the selection start (0-based index) and second argument is the selection length.
Search Text
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction type will invoke the search text command on the text control in the text control register. The search is case sensitive.
SendKeys
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction type will attempt to execute the provided SendKeys statement. The provided argument is considered a string literal.
Unlock Focus
Description: This instruction type will tell the Virtual UI to unlock focus from the currently locked text control.
Virtual UI Namespace
Click
Description: This instruction type will attempt to click the left mouse button on a clickable point inside of the automation element in the automation element register.
Click Mouse Button
Arguments: Int, Int, Int
Description: This instruction type will attempt to click the specified mouse button at the screen coordinates provided.
Focus On
Description: This instruction type will attempt to set focus on the automation element in the automation element register.
Focus On Process
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction type will search for a process with the name provided by the string argument. If a process is found it will attempt to bring the main window of that process to the foreground.
Get Element
Arguments: String, String, String
Description: This instruction type will attempt to get the automation element described the provided arguments. The result is placed in the automation element register.
Get First Child Element
Description: This instruction type will attempt to get the first child automation element of the automation element in the automation element register. The result is placed in the automation element register.
Get Focused Element
Description: This instruction type will attempt to get the focused automation element. The result is placed in the automation element register.
Get Foreground Element
Description: This instruction type will attempt to get the foreground automation element. The result is placed in the automation element register.
Get Parent Element
Description: This instruction type will attempt to get the parent automation element of the automation element in the automation element register. The result is placed in the automation element register.
Press Key
Arguments: Int, Bool, Bool, Bool
Description: This instruction type will attempt to press the key stroke provided as an argument.
Invoke
Description: This instruction type will attempt to call the invoke command of the automation element in the automation element register. The automation element must implement the invoke pattern to use this instruction type.
Select Item
Description: This instruction type will attempt to call the select item command of the automation element in the automation element register. The automation element must implement the selection item pattern to use this instruction type.
Set Value
Arguments: String
Description: This instruction type will attempt to call the set value command of the automation element in the automation element register. The automation element must implement the value pattern to use this instruction type.
Toggle
Description: This instruction type will attempt to call the toggle command of the automation element in the automation element register. The automation element must implement the toggle pattern to use this instruction type.
The Command Content Page & Instructions Editor
Overview
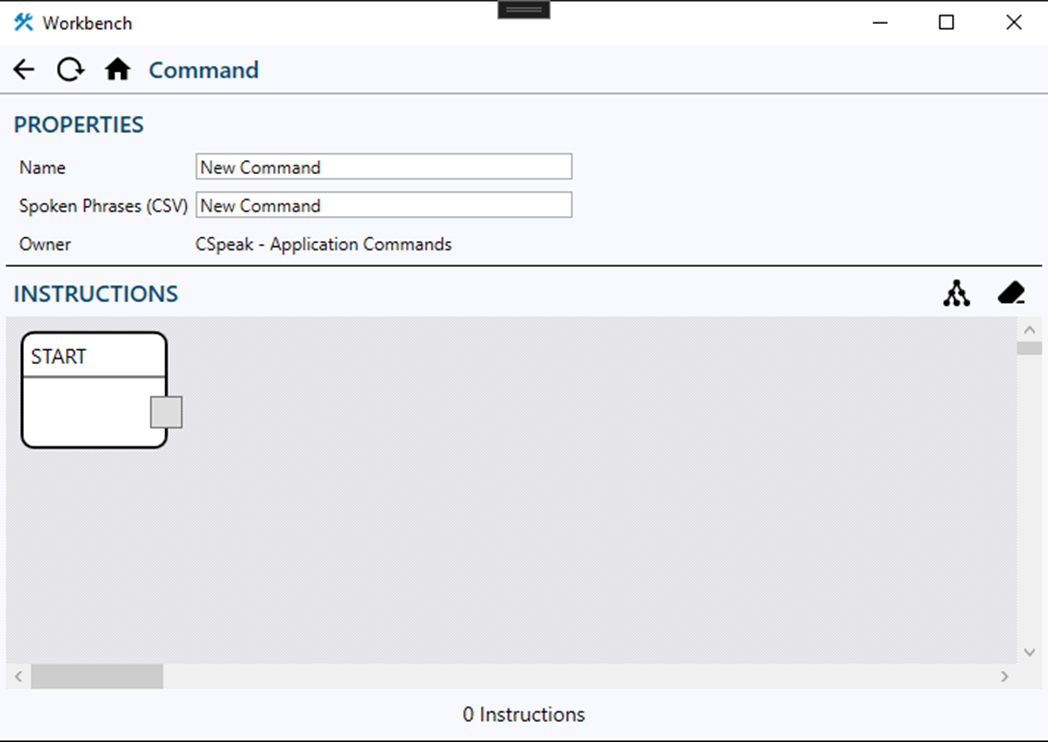
To help users create and test their commands a new visual interface has been created that will allow users to create instruction trees visually and help them understand how the instructions are flowing.
When the command content page is opened you will see a familiar layout that has the properties of the entity at the top. The second panel is the instructions editor.
Instructions Editor
The instructions editor is comprised of a small collection of components. The toolbar at the top has the trace button that will visually show the instruction flow for the command as presented in the editor. This function will also alert the user if an issue is found with the command. The top toolbar also has the clean button. This button will remove any instruction nodes that are not connected to the instruction flow. This serves as a quick and easy way to clean up commands after testing. Inside the instructions panel you will see the start node. All commands have a starting node that can be found in the top left of the instructions panel. The starting node serves as instruction zero and allows you to start your instruction flow.
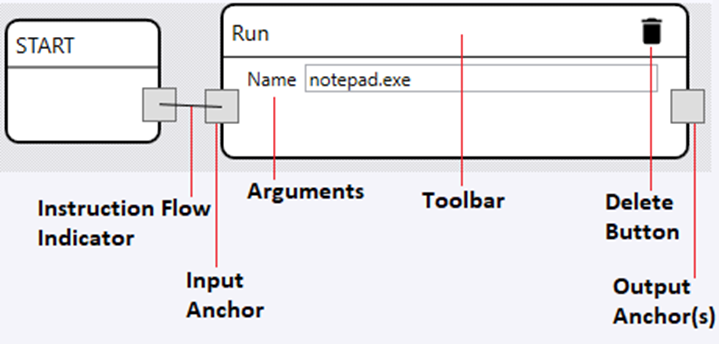
Instruction Nodes
To add instructions to your command, right click on the instructions panel and select the desired instruction to add. After the instruction is added you can click and drag on the toolbar to move the instruction. To remove an instruction, click on the delete button. If an instruction has arguments, they will be shown in the middle of content panel of the instruction. All instructions will have a single input anchor. To connect to instructions, you must click and drag from the output anchor of one instruction to the input anchor of the target instruction. Instructions can have between 0 and infinite output anchors. In general, instructions with more than 1 output anchors will be found in the control structures namespace.
Common Issues
Circular References
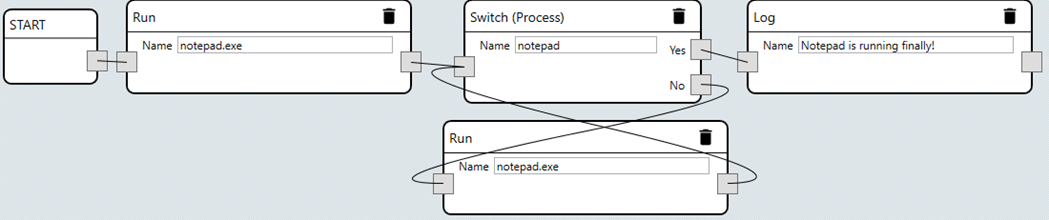
A circular reference is when an instruction tree has a node that is referenced by more than one node. This can either be in the form of a looping instruction branch or an instruction used by the same output anchor. If left unchecked this can cause a process to run out of memory and crash. To avoid this situation a command will not be allowed to save if a circular reference exists.
Maximum Instruction Depth
To avoid long running or resource intensive operations and instruction flows there is an imposed maximum depth that an instruction workflow may use. Since instruction flows can branch it is not a constant limit, but generally speaking you can expect the editor to warn you about maximum depth around 28 linear instructions.
No Starting Instruction
This occurs when the first instruction is not tied to the start instruction node. To resolve this all you must do is connect the start instruction node to your first instruction.
Recursion
This occurs when a workflow has a use command instruction that calls the containing command. To resolve this, you must remove the instruction or point the instruction to a different command.